Regional Variations in the Efficient Deployment of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement as a CDR Method
This week, we are taking a closer look at the paper that has been published in Nature Climate Change. The study was led by Mengyang Zhou and Michael D. Tyka from the University of Connecticut in the USA and used computer models to map the timescales and efficiency of carbon removal via OAE at global scale, revealing important regional differences.
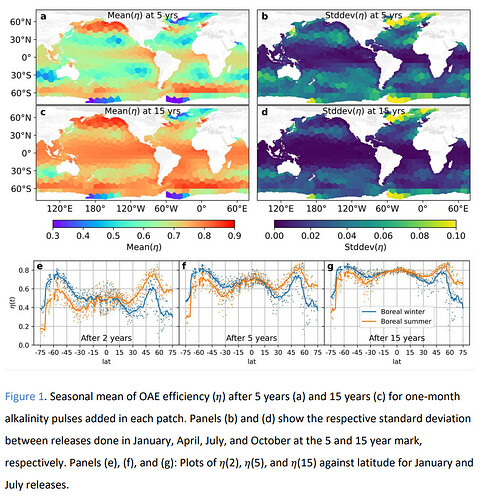
Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE) is a method that can significantly contribute to the achievement of CDR at scale. That said, it may be challenging to achieve a complete air-sea CO₂ equilibrium. The failure to achieve this equilibrium can adversely impact the efficiency of the carbon removal process. Due to this reason, the authors have created the first map showcasing the efficiency of OAE at a global scale. In doing so, they have also demonstrated the extent to which seasonal changes can impact OAE efficiency. As a result, they have determined two factors that play a crucial role in the successful deployment of OAE, namely the latitude and season during which alkalinity is released. In addition, they have made quantifications with respect to the locations where OAE is deployed as well as the timescales during which such deployment takes place. This measurement has allowed them to determine the prerequisites for integrating OAE models into regional ocean models.
Some conclusions from this study:
-
The rate at which the deployment of OAE can efficiently remove carbon depends on the speed of gas transfer as well as the processes leading to the movement of the Earth’s lithospheric plate and its re-appearance determining the quantity of alkalinity maintained in the surface.
-
Variations stemming from seasons and locations gradually impacted the efficiency of OAE deployment to a lower extent.
-
In some regions, CO2 re-equilibration takes place at the local level and at a rapid pace without being influenced by seasonal variations. Regions exhibiting such features can be ideal locations for carrying out the first experimental studies geared towards OAE deployment.
-
The map provided by this study can be utilized in the future for assessing the market quality of monitoring, reporting and verification schemes.
-
The analysis of the outcomes of this research in conjunction with data laying down technical and economic barriers can be utilized as a roadmap for assessing the viability of OAE deployment.
Read the full paper here: Mapping the Global Variation in the Efficiency of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement for Carbon Dioxide Removal I ResearchGate I Nature Climate Change